Habitats for all
The Urrbrae Wetland has been planted with over 100 different species of plants that are considered "local" or endemic to the area; that is they are believed to have grown in the area prior to European settlement in 1836. This has created an overall landscape of native bushland that represents a grey box grassy woodland and contains tall trees, shrubs, grasses, shoreline plants and water plants.
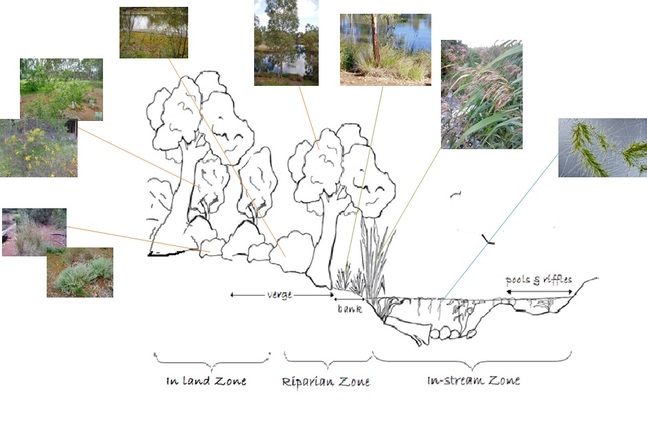
Fresh water environments, like the one that's been create here at the wetland, is an example of an ecosystem that provides a number of different habitats. These habitats vary along the water course due to factors including water flow, topography, soils and human impacts.
Fresh water habitats are often divided into zones to make studying them easier. There are 3 main zones here at the Urrbrae Wetland:
1. Inland Zone - grey box grassy woodland
2. Riparian Zone - terrestrial meets aquatic
3. In-stream Zone - in the water
The vegetation types present at the Urrbrae Wetland not only provide habitat for native animals but help slow the speed of the water which aids the sedimentation process. Many of the riparian and in stream plants are able to absorb substances including nitrates and phosphates, thus removing them from the water. The distinct habitat zones also provides a valuable resource for conducting controlled experiments to discover preferred habitat types.
Fresh water environments, like the one that's been create here at the wetland, is an example of an ecosystem that provides a number of different habitats. These habitats vary along the water course due to factors including water flow, topography, soils and human impacts.
Fresh water habitats are often divided into zones to make studying them easier. There are 3 main zones here at the Urrbrae Wetland:
1. Inland Zone - grey box grassy woodland
2. Riparian Zone - terrestrial meets aquatic
3. In-stream Zone - in the water
The vegetation types present at the Urrbrae Wetland not only provide habitat for native animals but help slow the speed of the water which aids the sedimentation process. Many of the riparian and in stream plants are able to absorb substances including nitrates and phosphates, thus removing them from the water. The distinct habitat zones also provides a valuable resource for conducting controlled experiments to discover preferred habitat types.
Incoporating a trip to the Urrbrae Wetlands
There are a great number of ecological concepts that can be brought to life at the Urrbrae Wetland. These include concepts centred around:
- Food webs and food chains
- Interdependence
- Population and habitat studies
- Symbiotic relationships
- Adaptation
- Dispersion and abundance related to particular abiotic factors
and many, many more.
Below are a few ideas that could be investigated in conjucnction with a trip to the wetlands:
- How might water habitats change over time?
- Predict how aquatic macroinvertebrates might adapt to survive in the future?
- What would happen if all pesticides were banned?
- Plan, draw or construct a healthy water environment for the future?
- Food webs and food chains
- Interdependence
- Population and habitat studies
- Symbiotic relationships
- Adaptation
- Dispersion and abundance related to particular abiotic factors
and many, many more.
Below are a few ideas that could be investigated in conjucnction with a trip to the wetlands:
- How might water habitats change over time?
- Predict how aquatic macroinvertebrates might adapt to survive in the future?
- What would happen if all pesticides were banned?
- Plan, draw or construct a healthy water environment for the future?
To discuss how you could explore some of these ideas or another area of your curriculum simply call the Wetland Manager and start creating a unique learning opportunity that is tailored to your needs